Diagonalizable Linear Transformation
Definition 1
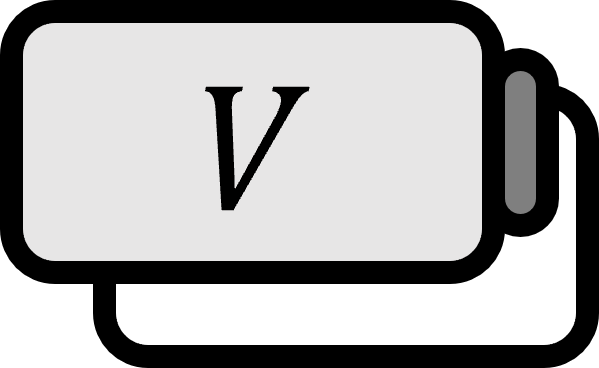
Let $V$ be called a finite-dimensional vector space. Let $T : V \to V$ be called a linear transformation. If there exists an ordered basis $\beta$ for which the matrix representation $\begin{bmatrix} T \end{bmatrix}_{\beta}$ of $T$ becomes a diagonal matrix, $T$ is said to be diagonalizable.
For a square matrix $A$, if the $L_{A}$ is diagonalizable, then the matrix $A$ is said to be diagonalizable.
Explanation
Suppose the linear transformation $T : V \to V$ is diagonalizable. Let $\beta = \left\{ v_{1}, \dots, v_{n} \right\}$ be an ordered basis of $V$. And let $D = \begin{bmatrix} T \end{bmatrix}_{\beta}$ be a diagonal matrix. Then, for each $v_{j} \in \beta$, we obtain the following.
$$ T(v_{j}) = \sum_{i} D_{ij} v_{i} = D_{jj}v_{j} $$
If it is said that $\lambda_{j} = D_{jj}$,
$$ T(v_{j}) = \lambda_{j} v_{j} $$
The elements of the ordered basis that make $\begin{bmatrix} T \end{bmatrix}_{\beta}$ a diagonal matrix satisfy such a special form of equation. Therefore, the vectors represented by such an ordered basis $\beta$ simply involve multiplying each component by the scalar $\lambda_{j}$, which is the same as applying the linear transformation $T$. These special vectors $v_{j}$ and scalars $\lambda_{j}$ are called eigenvectors and eigenvalues, respectively. Thus, if we relate the condition of being diagonalizable to eigenvalues,
Existence of $n$ linearly independent eigenvectors = Existence of a basis of eigenvectors $\iff$ diagonalizable
Stephen H. Friedberg, Linear Algebra (4th Edition, 2002), p245-246 ↩︎