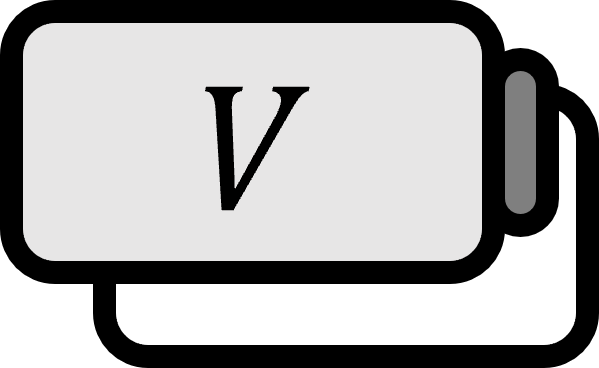
Linear Transformation
Definition1
A transformation is when a function $T : V \to W$ maps from one vector space to another, that is $V$, $W$ are both vector spaces, we call $T$ a transformation.
If the transformation $T$ is a linear function, satisfying the following two conditions for any $\mathbf{v},\mathbf{u} \in V$ and scalar $k$, it is called a linear transformation:
- $T(k \mathbf{u}) = k T(\mathbf{u})$
- $T(\mathbf{u} + \mathbf{v}) = T(\mathbf{u}) + T(\mathbf{v})$
Specifically, if $W=\mathbb{C}$, then $T$ is called a linear functional.
Explanation
Functions, mappings, transformations are essentially synonymous. However, in contexts involving vector spaces like linear algebra or functional analysis, the term transformation is primarily used, abbreviated as $T$.
Linear transformations from finite dimensions to finite dimensions are often treated like matrix multiplication, depicted as follows:
$$ T(\mathbf{x}) = T\mathbf{x} $$
A linear transformation that satisfies $T : V \to V$ on $V$ is sometimes called a linear operator on $V$. However, it doesn’t always have to be that the domain and codomain are identical to be called an operator. For practical reasons, several textbooks define $T : V \to V$ as a linear operator.
$$ \text{linear transformation form } V \text{ to } V \to \text{linear operator on } V $$
The set of all linear transformations from vector space $X$ to $Y$ is denoted as follows: $L(X, Y)$2.
$$ L(X,Y) = \mathcal{L}(X, Y) := \left\{ T : X \to Y\enspace |\enspace T \text{ is linear } \right\} $$
Matrix transformation is a type of linear transformation.
Identity Transformation
A linear transformation $I : V \to V$ satisfies
$$ I(\mathbf{v}) = \mathbf{v} $$
for all $\mathbf{v} \in V$ is called an identity transformation. Specifically, it might be denoted as $I_{V}$.
Zero Transformation
A linear transformation $T_{0} : V \to W$ satisfies
$$ T_{0}(\mathbf{v}) = \mathbf{0}_{W} $$
for all $\mathbf{v} \in V$ is called a zero transformation. Here, $\mathbf{0}_{W}$ is the zero vector in $W$. Also denoted as $O$, $0$, it is essentially a zero function.
Properties
If $T : V \to W$ is a linear transformation, then the following hold:
(a) $T(\mathbf{0}) = \mathbf{0}$
(b) For all $\mathbf{u}, \mathbf{v} \in V$, $T(\mathbf{u} - \mathbf{v}) = T(\mathbf{u}) - T(\mathbf{v})$
(c) $T$ is injective $\iff$ $\ker T$ $= \left\{ \mathbf{0} \right\}$
Proof
(a)
By the property of vector spaces, since $0\mathbf{v} = \mathbf{0}$,
$$ T(\mathbf{0}) = T( 0\mathbf{u}) = 0T(\mathbf{u}) = \mathbf{0} $$
■
(b)
Similarly, due to the property of vector spaces that $-\mathbf{v} = (-1)\mathbf{v}$,
$$ \begin{align*} T(\mathbf{u} - \mathbf{v}) &= T \big( \mathbf{u} + (-1)\mathbf{v} \big) \\ &= T(\mathbf{u}) + T\big( (-1)\mathbf{v} \big) \\ &= T(\mathbf{u}) + (-1)T(\mathbf{v}) \\ &= T(\mathbf{u}) - T(\mathbf{v}) \end{align*} $$
■
(c)
■