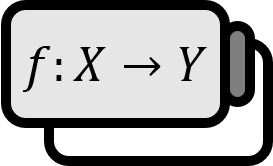Linear Function
Definition
A function $f : X \to Y$ is called linear if it satisfies the following two conditions for $x,x_{1},x_{2}\in X$ and $a \in \mathbb{R}$,
- $f(ax) = af(x)$
- $f(x_{1} + x_{2}) = f(x_{1}) + f(x_{2})$
Explanation
If it is not linear, it is called nonlinear. The two conditions are sometimes combined as follows
$$ f(ax_{1} + x_{2}) = af(x_{1}) + f(x_{2}) $$
If in 2., instead of being equal, it satisfies being less than or equal to $\le$, it is called quasilinear.
Bilinear
If a bivariate function $f = f(x,y)$ is linear with respect to each variable, it is called bilinear.
Multilinear
If a multivariate function $f= f(x_{1}, \dots, x_{n})$ is linear with respect to each variable, it is called multilinear.