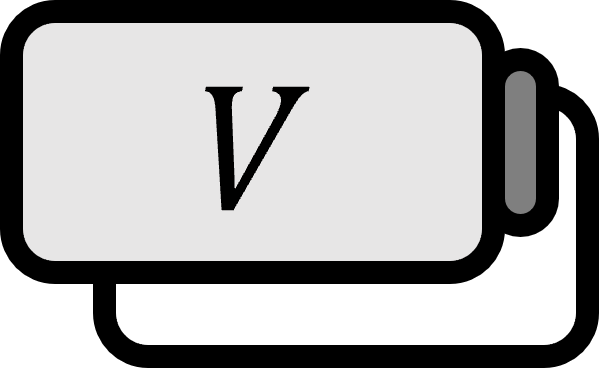
零行列の固有値はゼロのみである
Proof
English Translation:
Assume that $T$ is a nilpotent such that $T^{k} = T_{0}$. $T_{0}$ is a zero transformation. Moreover, let’s denote $\lambda$ as the eigenvalue of $T$, and the corresponding eigenvector as $\mathbf{v} \in V$.
$$ T\mathbf{v} = \lambda \mathbf{v} $$
Taking $T^{k-1}$ on both sides gives us $T^{k-1}(T\mathbf{v}) = T^{k-1}(\lambda \mathbf{v})$. Starting with the left side, we can arrange it as follows.
$$ T^{k-1}(T\mathbf{v}) = T^{k}(\mathbf{v}) = T_{0}\mathbf{v} = \mathbf{0} $$
Here, $\mathbf{0}$ is the zero vector of vector space $V$. Organizing the right side, since $T$ is a linear transformation, we get:
$$ T^{k-1}(\lambda \mathbf{v}) = \lambda T^{k-1}\mathbf{v} = \lambda T^{k-2}(T\mathbf{v}) = \lambda T^{k-2}(\lambda \mathbf{v}) = \lambda^{2}T^{k-2}\mathbf{v} = \cdots = \lambda^{k-1}\mathbf{v} $$
Therefore, we obtain the following.
$$ \mathbf{0} = \lambda^{k-1}\mathbf{v} $$
However, since $\mathbf{v}$ is an eigenvector, it is not a zero vector. Hence, for the above equation to hold:
$$ \lambda^{k-1} = 0 \implies \lambda = 0 $$
■
Japanese Translation:
$T$が$T^{k} = T_{0}$である冪零だと仮定しよう。$T_{0}$は零変換だ。そして、$\lambda$を$T$の固有値、これに対応する固有ベクトルを$\mathbf{v} \in V$としよう。
$$ T\mathbf{v} = \lambda \mathbf{v} $$
両辺に$T^{k-1}$をとると、$T^{k-1}(T\mathbf{v}) = T^{k-1}(\lambda \mathbf{v})$だ。左辺から整理すると、以下のようになる。
$$ T^{k-1}(T\mathbf{v}) = T^{k}(\mathbf{v}) = T_{0}\mathbf{v} = \mathbf{0} $$
ここで、$\mathbf{0}$はベクトル空間$V$の零ベクトルだ。右辺を整理すると、$T$が線形変換であるため、以下のようになる。
$$ T^{k-1}(\lambda \mathbf{v}) = \lambda T^{k-1}\mathbf{v} = \lambda T^{k-2}(T\mathbf{v}) = \lambda T^{k-2}(\lambda \mathbf{v}) = \lambda^{2}T^{k-2}\mathbf{v} = \cdots = \lambda^{k-1}\mathbf{v} $$
よって、以下を得る。
$$ \mathbf{0} = \lambda^{k-1}\mathbf{v} $$
しかし、$\mathbf{v}$は固有ベクトルであるため、零ベクトルではない。したがって、上記の式が成り立つためには:
$$ \lambda^{k-1} = 0 \implies \lambda = 0 $$
■