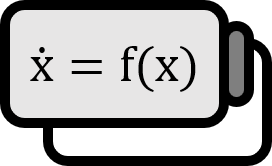Tipping Points in Dynamics
Terminology
In dynamical systems, experiencing a sudden transition from one state to another is referred to as the phenomenon of tipping point1.
Description
The phenomenon of tipping point is discussed primarily in contexts where returning to the original state after a transition is impossible. Examples include a sudden deterioration from a healthy state (in physiology), abrupt extinction of species (in ecology), or the melting of Arctic glaciers (in climatology). Although the tipping point concept emphasizes ‘sudden changes’ rather than directly addressing irreversibility, most cases usually involve hysteresis. To avoid confusion with terminology, it can be summarized as follows:
- Fold Bifurcation: The tipping point is akin to the turning point in fold bifurcation, accompanied by hysteresis. Most phenomena of academic interest fall into this category.
- Slow but irreversible transitions: Involves hysteresis but cannot be termed as a tipping point phenomenon.
- Rapid transitions, even if reversible: If there is a sudden change at a point, it is a tipping point, but not hysteresis.
See Also
Panahi. (2023). Rate-induced tipping in complex high-dimensional ecological networks: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2308820120 ↩︎