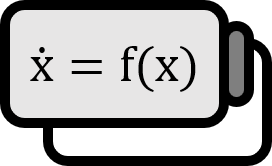Representing Dynamical Systems and Fixed Points with Maps
Definitions1
- A function $f : X \to X$ whose domain and codomain are the same is called a Map. A map that is the composition of $f$ $k$ times is denoted as $f^{k}$.
- $p \in X$ that satisfies $f(p) = p$ is called a Fixed Point.
- If there exists a $\epsilon > 0$ that satisfies $\displaystyle \lim_{k \to \infty} f^{k} (x) = p$ for all $x \in N_{ \epsilon } ( p )$, then the fixed point $p$ is called a Sink.
- If there exists a $\epsilon > 0$ that satisfies $f^{ \infty } (x) \notin N_{\epsilon } (p)$ for all $x \in N_{\epsilon } (p)$ except $p$, then the fixed point $p$ is referred to as a Source.
- $N_{ \epsilon } ( p ) = B ( p ; \epsilon )$ refers to the neighborhood containing all points within the radius $\epsilon$ of $p$.
Examples
- The map defined by $X$ forms a dynamical system by mapping each point $x_{t-1}$ to $x_{t}$. A simple example is a point that moves $60$ in direction $x$ whenever time $t$ changes by $1$. The position of this point can be represented as follows. $$ x_{t} = f(x_{t-1}) = x_{t-1} + 60 $$
- Another example of a map is $f(x) = x^3$, which means that $0$ and $\pm 1$ are fixed points.
- Among them, every number in the sufficiently small interval $( - 1, 1)$ including $0$ becomes smaller when squared and eventually converges to $0$, making it a sink.
- Thinking of any interval that includes $\pm 1$, if its size is greater than $1$, the magnitude increases each time it is cubed, making it a source.
A sink is a sort of ‘convergence point’ where nearby points gather, while a source is a sort of ‘divergence point’ where points that were close begin to move away from each other. Therefore, a sink is also called a Stable fixed point, and a source is called an Unstable fixed point.
This is similar to the sink and source in graph theory.
See Also
- Dynamical systems expressed by maps
- Dynamical systems expressed by differential equations
- Rigorous definition of dynamical systems
Yorke. (1996). CHAOS: An Introduction to Dynamical Systems: p5, 9. ↩︎