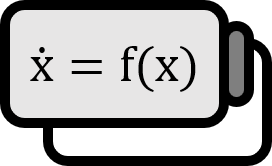Transcritical Bifurcation
Definition 1 2
Transcritical Bifurcation is a bifurcation in a dynamical system where two fixed points exchange stability as a parameter of the system varies.
Normal Form
The normal form of a transcritical bifurcation is given by: $$ \dot{x} = rx - x^{2} $$
Diagram
The bifurcation diagram of a transcritical bifurcation is as follows:

Explanation
The normal form of a transcritical bifurcation always has two fixed points, $x_{1} = 0$ and $x_{2} = r$, regardless of $r$. The exchange of stability between the two fixed points means that at the critical point $r = 0$, the stability of fixed points $x_{1} = 0$ and $x_{2} = r$ reverses.
- $r < 0$: $x_{1} = 0$ is stable and $x_{2} = r$ is unstable.
- $r = 0$: The two fixed points merge and become a saddle node. At $\dot{x} = -x^{2}$, because $x$ is always negative, trajectories converge to $x_{1} = 0$ in $x > 0$ and diverge from $x_{1} = 0$ in the negative direction in $x < 0$.
- $r > 0$: $x_{1} = 0$ is unstable and $x_{2} = r$ is stable.