Rate of Convergence in Numerical Analysis
Definition 1
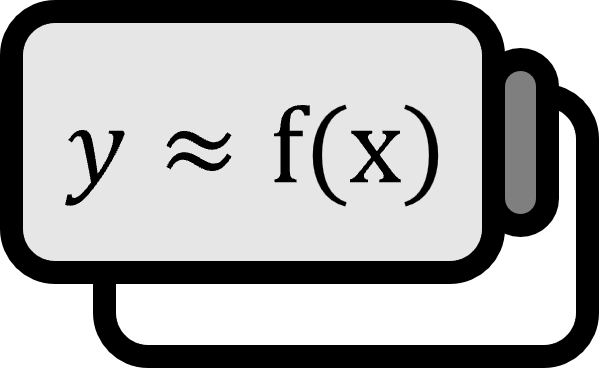
If there exists a constant $c \ge 0$ such that the sequence $\left\{ x_{n} \right\}$ converging to $\alpha$ satisfies $$ | \alpha - x_{n+1} | \le c | \alpha - x_{n} | ^{p} $$ for the order of convergence $p \ge 1$, then $\left\{ x_{n} \right\}$ is said to converge to $\alpha$ at the rate of $c$ of order $p$.
Explanation
In particular, together with the condition $c < 1$, if $p=1$ then it is called Linear Convergence. Similarly, when $p=2$ it is called Quadratic Convergence, and when $p=3$ it is called Cubic Convergence.
In pure analysis, one might only care about whether a sequence converges, but in numerical analysis, the rate of convergence is also important.
Atkinson. (1989). An Introduction to Numerical Analysis(2nd Edition): p56. ↩︎