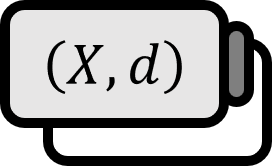Balls and Open Sets, Closed Sets in Metric Spaces
Definition
Given a metric space where $\left( X, d \right)$, let $a \in X$ and $r > 0$.
- An open ball with center $a$ and radius $r$ is denoted by $B_{d} (a,r) = \left\{ x \in X \ | \ d(a,x) < r \right\}$.
- A closed ball with center $a$ and radius $r$ is denoted by $B_{d} [a,r] = \left\{ x \in X \ | \ d(a,x) \le r \right\}$.
- If $O \subset X$ is a union of open balls, then $O$ is called an open set in $X$.
- If $X \setminus C$ is an open set for $C \subset X$, then $C$ is called a closed set in $X$.
Explanation
Open and closed sets can be defined differently, but essentially, they are similar concepts.
The term “ball” generalizes the concepts of intervals, open intervals, and closed intervals. Considering that an interval can also be thought of as a $1$-dimensional ball, this is an intuitive link. Moreover, this generalization doesn’t just stop with dimensions in Euclidean spaces denoted by $\mathbb{R}$; as long as distance is properly defined, it is well established anywhere.
Open and closed sets generally satisfy the following properties:
Properties
Let us denote the open sets in the entire space $X$ as $O_{\alpha}$, and the closed sets as $C_{\alpha}$.
- [1]: $X$ and $\emptyset$ are both open and closed.
- [2]: The union of open sets $\displaystyle \bigcup_{\alpha \in \forall} O_{\alpha}$ is an open set in $X$.
- [3]: The finite intersection of open sets $\displaystyle \bigcap_{i = 1}^{n} O_{i} $ is an open set in $X$.
- [4]: The intersection of closed sets $\displaystyle \bigcap_{\alpha \in \forall} C_{\alpha}$ is a closed set in $X$.
- [5]: The finite union of closed sets $\displaystyle \bigcup_{i = 1}^{n} C_{i}$ is a closed set in $X$.
Without the condition of being finite in [3], $\displaystyle \bigcap_{n = 1}^{ \infty } \left( -{{1} \over {n}} , {{1} \over {n}} \right) = \left\{ 0 \right\}$ could be given as a counterexample. Without the condition of being finite in [5], $\displaystyle \bigcup_{n = 1}^{ \infty } \left[ 0 , 1-{{1} \over {n}} \right] = [ 0 , 1 )$ could be given as a counterexample.
Proof
[1]
Introduced in this post.
[2]~[5]
Introduced in this post.