Mapping to the Quotient Space
Theorem1
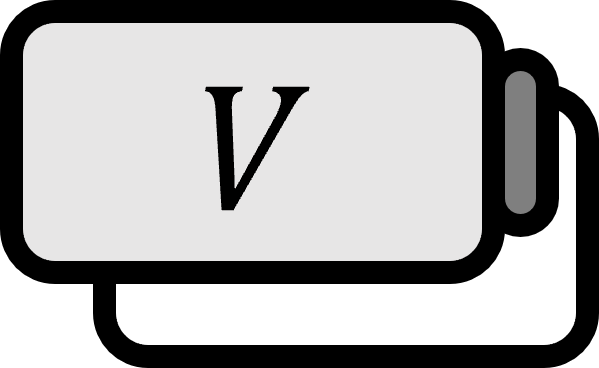
Let $V$ be a vector space, and $W \le V$ a subspace. Define the function $\eta$ as follows.
$$ \begin{align*} \eta : V &\to V/W \\ v &\mapsto v + W \end{align*} $$
In this case, $V/W$ is the quotient space of $V$. Then
$\eta$ is a linear transformation and its null space is $N(\eta) = W$.
If $V$ is finite-dimensional, then
$$ \begin{equation} \dim(W) + \dim(V/W) = \dim(V) \end{equation} $$
Explanation
The result on dimensions $(1)$ can also be obtained by a different proof.
Proof
The following holds, so $\eta$ is a linear transformation.
$$ \begin{align*} \eta (av + u) &= (av + u) + W \\ &= (av + W) + (u + W) \\ &= a(v + W) + (u + W) \\ &= a\eta (v) + \eta (u) \\ \end{align*} $$
The null vector of $V/W$ is $W$. For any $w \in W$, since $w + W = W$ holds, $N(\eta) = W$ is established. Also, for any $v + W \in V/W$, since $v \in V$ exists, the range of $\eta$ is $R(\eta) = V/W$. Then, by the dimension theorem,
$$ \begin{align*} &&\rank(\eta) + \nullity(\eta) &= \dim(V) \\ \implies &&\dim(R(\eta)) + \dim(N(\eta)) &= \dim(V) \\ \implies &&\dim(V/W) + \dim(W) &= \dim(V) \\ \end{align*} $$
■
Stephen H. Friedberg, Linear Algebra (4th Edition, 2002), p79 ↩︎