Multiplicity of Eigenvalues of Linear Transformations
Definition1
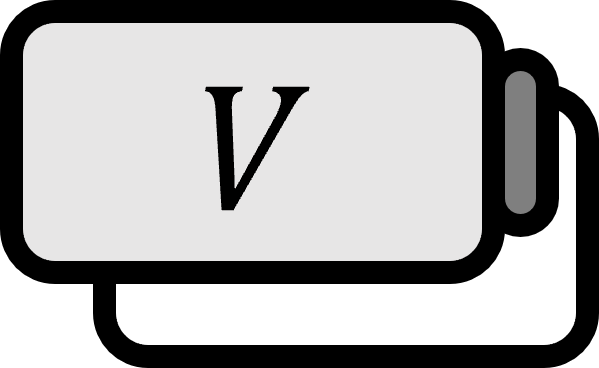
Let $V$ be a finite-dimensional vector space, and let $T : V \to V$ be a linear transformation. Let $f(t)$ be the characteristic polynomial of $T$, and let $\lambda$ be an eigenvalue of $T$. The highest power $k$ of the factor $(t - \lambda)^{k}$ in $f(t)$ is called the (algebraic) multiplicity of $\lambda$.
Explanation
Simply put, the multiplicity of an eigenvalue refers to how many times $\lambda$ is a root of the characteristic polynomial $f(t)$. So, if $f(t)$ is a linear transformation on a $n$-dimensional vector space, the multiplicity $k$ of the eigenvalue $\lambda$ is $1 \le k \le n$.
The dimension of the eigenspace $E_{\lambda}$ corresponding to the eigenvalue $\lambda$ is called the geometric multiplicity of $\lambda$. Typically, unless otherwise stated, multiplicity refers to algebraic multiplicity.
See Also
Stephen H. Friedberg, Linear Algebra (4th Edition, 2002), p263 ↩︎