Properties of Bounded Linear Operators
Theorem1
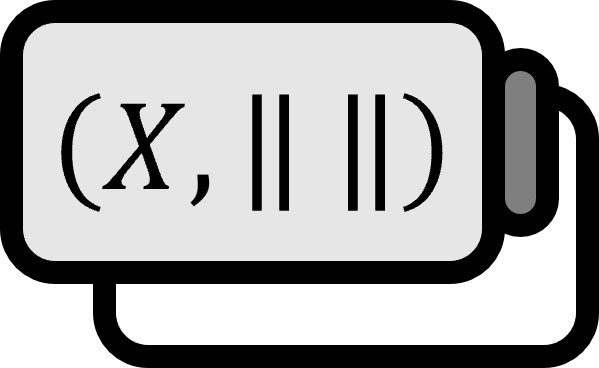
Let’s denote $V$ as normed space, $T$ as bounded linear operator, and $W \subset V$. Then, the following holds:
(a)
$$ T\left( \overline{W} \right) \subset \overline{T(W)} $$
Moreover, if $T$ is invertible, and $T^{-1}$ is also a bounded linear operator, then the following is true:
$$ T\left( \overline{W} \right) = \overline{T(W)} $$
Here, $\overline{W}$ is the closure of $W$.
(b)
Let $\left\{ \mathbf{v}_{k} \right\}$ be a sequence in $V$, and $\mathbf{v} \in V$. Then, the following holds:
$$ \lim \limits _{k \to \infty} \mathbf{v}_{k} = \mathbf{v} \implies \lim \limits _{k \to \infty} T\mathbf{v}_{k} = T\mathbf{v} $$
(c)
Assuming that for a sequence $\left\{ \mathbf{v}_{k} \right\}$ in $V$ and some constant $\left\{ c_{k} \right\}$, $\sum \limits_{k=1}^{\infty} c_{k}\mathbf{v}_{k}$ converges. Then, the following is true:
$$ T \sum \limits_{k=1}^{\infty} c_{k} \mathbf{v}_{k} = c_{k} \sum \limits_{k=1}^{\infty} T \mathbf{v}_{k} $$
Explanation
A bounded operator is continuous, and (b) is an obvious fact since it is the equivalency condition for the function to be continuous.
Proof
(b)
Since $T$ is bounded and linear, the following equation holds:
$$ \left\| T \mathbf{v}_{k} - T \mathbf{v} \right\| = \left\| T (\mathbf{v}_{k} - \mathbf{v}) \right\| \le \left\| T \right\| \left\|\mathbf{v}_{k} - \mathbf{v} \right\| $$
Therefore, if $\mathbf{v}_{k} \to \mathbf{v}$, then $T \mathbf{v}_{k} \to T \mathbf{v}$.
■
Ole Christensen, Functions, Spaces, and Expansions: Mathematical Tools in Physics and Engineering (2010), p45 ↩︎