Rank, Nullity, and Dimension Theorems of Linear Transformations
Definition1
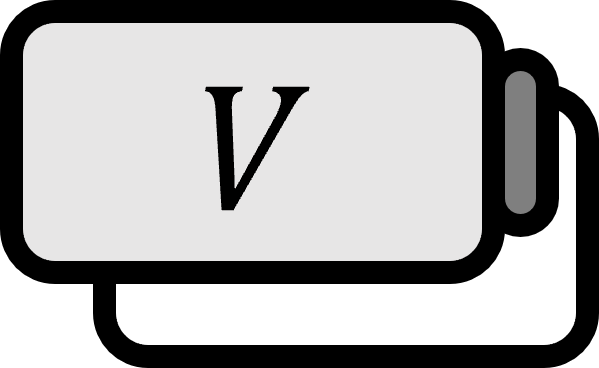
Let $T : V \to W$ be a linear transformation.
If the range $R(T)$ of $T$ is finite-dimensional, the dimension of $R(T)$ is called the rank of $T$, denoted by:
$$ \mathrm{rank}(T) := \dim (R(T)) $$
If the null space $N(T)$ of $T$ is finite-dimensional, the dimension of $N(T)$ is called the nullity of $T$, denoted by:
$$ \mathrm{nullity}(T) := \dim\left( N(T) \right) $$
Explanation
This is a generalization of the notion of rank, nullity of matrices. In fact, if $V, W$ is finite-dimensional, then $T$ is essentially a matrix, and $N(T)$ is the null space of the matrix $M_{T}$ representing $T$. Since the nullity of a matrix is the dimension of its null space, the following holds:
$$ \mathrm{nullity}(T) = \dim\left( N(T) \right) = \dim (\mathcal{N}(M_{T})) $$
Generalizing the dimension theorem for matrices to linear transformations gives the following theorem.
Theorem
If $T : V \to W$ is a linear transformation and $V$ is finite-dimensional, the following holds:
$$ \mathrm{rank}(T) + \mathrm{nullity}(T) = \dim (V) $$
Howard Anton, Elementary Linear Algebra: Aplications Version (12th Edition, 2019), p455-456 ↩︎