Convergence of Sequences in Normed Spaces
Definition
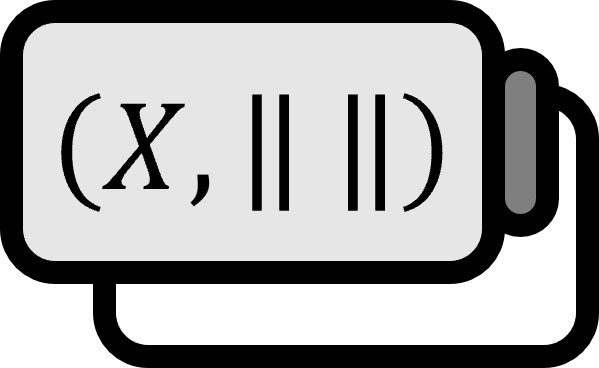
Let’s call $(X, \left\| \cdot \right\|)$ as a normed space. For a sequence $\left\{ x_{n} \right\}$ of $X$,
$$ \lim \limits_{n \to \infty} \left\| x - x_{n} \right\| = 0,\quad x\in X $$
it is said to converge to $x$ if it satisfies the following condition, and it is represented as follows.
$$ x_{n} \to x \text { as } n \to \infty \quad \text{or} \quad x=\lim \limits_{n\to\infty}x_{n} $$
Explanation
To define convergence, a distance is needed, but since distance can be naturally defined as $d(x,y)=\left\| x - y \right\|$ in normed spaces (../1840), it’s similar to the definition in metric spaces except that the metric is replaced with a norm.
If for every $\epsilon >0$, there exists a natural number $N\in \mathbb{N}$ satisfying the equation below, then the sequence $\left\{ x_{n} \right\}$ is said to converge to $x$.
$$ \left\| x - x_{n} \right\|<\epsilon \quad \forall n \ge N $$
Compared to weak convergence, it is also referred to as strongly converging.
$$ \begin{align*} & x_{n} \text{ converges to } x \\ =&\ x_{n} \text{ converges in norm to } x \\ =&\ x_{n} \text{ converges strongly to } x \end{align*} $$