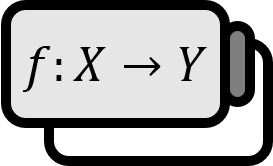Dirichlet eta function
Definition
The function $\eta : \mathbb{C} \to \mathbb{C}$ defined as below is called the Dirichlet eta Function. $$ \eta (s) := \sum_{n \in \mathbb{N}} (-1)^{n-1} n^{-s} $$
The Dirichlet eta function is defined as the alternating Riemann zeta function.
Theorems
- [1] Relationship with the Riemann zeta function: $$ \eta (s) = \left( 1 - 2^{1-s} \right) \zeta (s) $$
- [2] Relationship with the gamma function: If $\operatorname{Re} (s) > 1$, then $$ \eta (s) \Gamma (s) = \mathcal{M} \left[ {{ 1 } \over { e^{x} + 1 }} \right] (s) = \int_{0}^{\infty} {{ x^{s-1} } \over { e^{x} + 1 }} dx $$
- $\re(z)$ represents the real part of the complex number $z \in \mathbb{C}$.
Proof
[1]
$$ \begin{align*} \zeta (s) - \eta (s) =& \sum_{n \in \mathbb{N}} {{ 1 } \over { n^{s} }} - \sum_{n \in \mathbb{N}} {{ (-1)^{n-1} } \over { n^{s} }} \\ =& \sum_{n \in \mathbb{N}} \left( {{ 1 } \over { n^{s} }} + {{ (-1)^{n} } \over { n^{s} }} \right) \\ =& 2 \sum_{n \in \mathbb{N}} {{ 1 } \over { (2n)^{s} }} \\ =& 2^{1-s} \sum_{n \in \mathbb{N}} {{ 1 } \over { n^{s} }} \\ =& 2^{1-s} \zeta (s) \end{align*} $$ Modifying for the Dirichlet eta function gives $$ \eta (s) = \left( 1 - 2^{1-s} \right) \zeta (s) $$
■
[2]
It is not so simple. Derived using the Dominated Convergence Theorem.
■