Fréchet Derivative
Definition
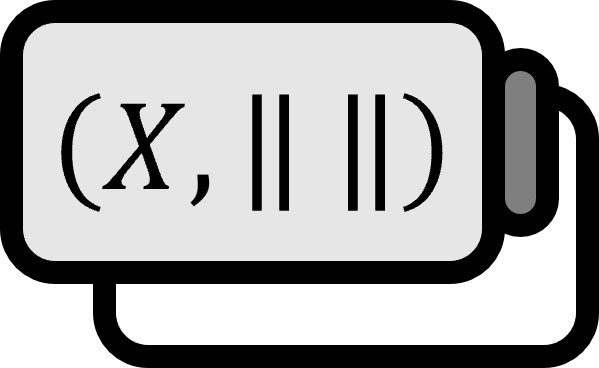
Given two Banach spaces $X, Y$ and an open set $\Omega \subset X$. Then a function $F : \Omega \to Y$ is said to be Frechet differentiable at $x\in \Omega$ if there exists a bounded linear operator $L : X \to Y$ that satisfies the following condition:
$$ \lim \limits_{ \left\| y \right \| \to 0} \frac{\| F(x+y) -F(x)-Ly \|}{\|y\|}=0 $$
In this case, such a linear transformation $L$ is unique and it is called the Frechet derivative of $F$ at $x$ and is denoted as follows:
$$ L = DF(x) = F^{\prime}(x) $$
Description
The Frechet derivative generalizes the concept of the total derivative to Banach spaces.
When dealing with normed spaces is trivial, one may omit “Frechet” and simply refer to it as differentiable or derivatives. Furthermore, since $y \to 0 \implies \|y\| \to 0$, it can be expressed as follows:
$$ \lim \limits_{ y \to 0} \frac{\| F(x+y) -F(x)-Ly \|}{\|y\|}=0 $$