What is a Norm Space?
Definition1
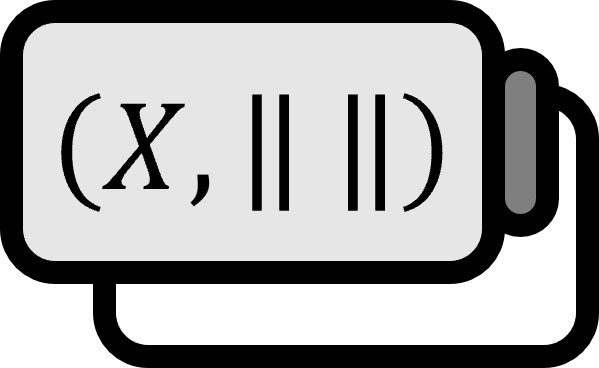
Let’s call $X$ a vector space. If there exists a function $\left\| \cdot \right\| : X \to \mathbb{R}$ that satisfies the following three conditions, then $\left\| \cdot \right\|$ is called the norm of $X$, and $(X,\left\| \cdot \right\| )$ is called a normed space.
(a) $\left\| x \right\| \ge 0,\quad \forall\ x \in X$ and $\left\| x \right\|=0 \iff x = 0$
(b) $\|cx\|=|c|\left\| x \right\|,\quad \forall\ x\in X,\ \forall\ c \in\mathbb{C}$
(c) $\left\| x + y \right\| \le \left\| x \right\| + \left\| y \right\|,\quad \forall\ x,y\in X$
Explanation
The norm of the normed space $X$ can be represented as below:
$$ \left\| x \right\|_{X},\quad \left\| x, X \right\|, \quad \left\| x ; X \right\| $$
(a) Without the condition of $\left\| x \right\|=0 \iff x = 0$, it becomes a seminorm.
(b) means that $\left\| x - y \right\| =\|y -x\|$ holds.
(c) is called the triangle inequality, and the inequality below is called the reverse triangle inequality. For normed spaces $(X, \left\| \cdot \right\| )$ and $x, y \in X$, the following inequality holds:
$$ \left| \left\| x \right\| - \left\| y \right\|\ \right| \le \left\| x- y \right\| $$
Normed Space as a Metric Space and Topological Space
Given a norm, a distance can be naturally defined. Therefore, a normed space becomes a metric space.
$$ d(x,y) = d_{X}(x,y) = \left\| x - y \right\|_{X} $$
Given the distance, an open ball can be defined as below:
$$ B_{d}(x,r)=B_{r}(x):=\left\{ y\in X\ :\ \left\| x - y \right\|_{X} <r \right\} $$
The collection of all open balls forms a basis in the topological sense on $X$. In other words, the open balls defined by the norm of $X$ can create a topology on $X$. This resulting topology on $X$ is called the norm topology2. Additionally, if the topology of topological vector space $X$ is the norm topology, $X$ is called normable.
In summary, saying that $X$ is a normed space implies that $X$ is a vector space, a metric space, and a topological space. Therefore, in functional analysis, a given normed space is naturally treated as a metric space and a topological space as well.
Proof3
By the triangle inequality,
$$ \left\| x \right\|= | (x-y) +y| \le |x-y| + \left\| y \right\| $$
holds. Therefore,
$$ \begin{equation} \left\| x \right\| - \left\| y \right\| \le \left\| x- y \right\| \end{equation} $$
Similarly,
$$ \left\| y \right\| = | (y - x) + x| \le \left\| y- x \right\| + \left\| x \right\| $$
thus,
$$ \begin{equation} \left\| y \right\| - \left\| x \right\| \le \left\| y- x \right\|=\left\| x - y \right\| \end{equation} $$
holds. Therefore, by $(1), (2)$,
$$ \left| \ \left\| x \right\| -\left\| y \right\|\ \right| \le \left\| x- y \right\| $$
■