Uniform Convexity
Definitions1
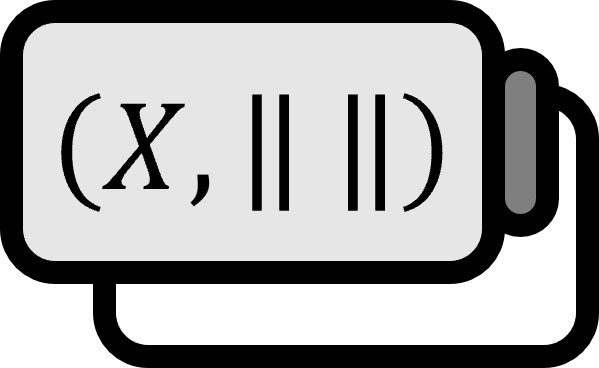
Let’s call $(X, \left\| \cdot \right\|)$ a normed space. We say that the norm $\left\| \cdot \right\|$ of $X$ is uniformly convex if it satisfies the following condition:
- For every $\epsilon$ where $0 \lt \epsilon \le 2$, there exists a positive number $\delta (\epsilon) \gt 0$ such that if $x,y \in X$ and $\| x \| = \|y\| = 1$, $\| x-y\| \ge \epsilon$ then it satisfies $\|( x+y)/2 \| \le 1-\delta (\epsilon)$.
In this case, the normed space $X$ itself is also considered to be uniformly convex. If a normable space has a uniformly convex norm, it is also said to be uniformly convex.
Explanation
It is important to note that just because some norm defined on $X$ is uniformly convex, does not mean that another equivalent norm is also uniformly convex.
Theorem
Hilbert space is uniformly convex.
Proof
Let us assume that a positive number $\epsilon$ is given where $0< \epsilon \le 2$. Assume that $H$ is a Hilbert space, and that $x,y \in H$, $\| x\|=\| y\|=1$, and $\| x-y\| \ge \epsilon$.
Parallelogram Law(../1842)
$$ \| x+ y \|^2 + \| x - y \|^2 = 2 \left( \| x \|^2 + \| y \|^{2} \right) $$
Substituting $x, y$ into the parallelogram law gives
$$ \| x+ y \|^2 + \| x - y \|^2 = 2 \left( \| x \|^2 + \| y \|^{2} \right) $$
$$ \implies \|x+y\|^2 =4-\|x-y\|^2\le 4-\epsilon^2 $$
$$ \implies \|x+y\|^2\le 4-\epsilon^2 $$
Summarizing,
$$ \| x+y\| \le \sqrt{4-\epsilon^2} \quad \implies \left\| \frac{x+y}{2} \right\| = \dfrac{1}{2}\|x+y \| \le \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{4-\epsilon^2} $$
Since $0 \lt \epsilon \le 2$, the range on the right-hand side is $0 \le \dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{4-\epsilon^2} \lt 1$. Therefore, as the Hilbert space is a complete space, it can be represented with some positive number $\delta (\epsilon)$ depending on $\epsilon$ as follows.
$$ \left\| \frac{x+y}{2} \right\| \le 1-\delta (\epsilon) $$
■
Robert A. Adams and John J. F. Foutnier, Sobolev Space (2nd Edition, 2003), p8 ↩︎