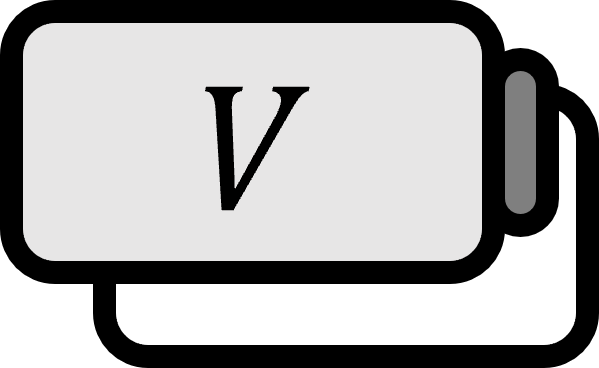
Translation
Definition
Let an element $\mathbf{u}$ of the vector space $V$ be given. The transformation $T_{\mathbf{u}} : V \to V$ below is called a translation.
$$ T_{\mathbf{u}}(\mathbf{v}) = \mathbf{v} + \mathbf{u} $$
Explanation
This is a canonical example of a transformation acting on a vector space that is not a linear transformation. Therefore, when the space is finite-dimensional, it cannot be represented by a matrix.
$$ T_{\mathbf{u}} (\mathbf{v} + \mathbf{w}) = \mathbf{v} + \mathbf{w} + \mathbf{u} \ne (\mathbf{v} + \mathbf{u}) + (\mathbf{w} + \mathbf{u}) = T_{\mathbf{u}}(\mathbf{v}) + T_{\mathbf{u}}(\mathbf{w}) $$
If you want to handle linear transformations that include translations, consider affine transformations.