Linear Functional
Definitions1
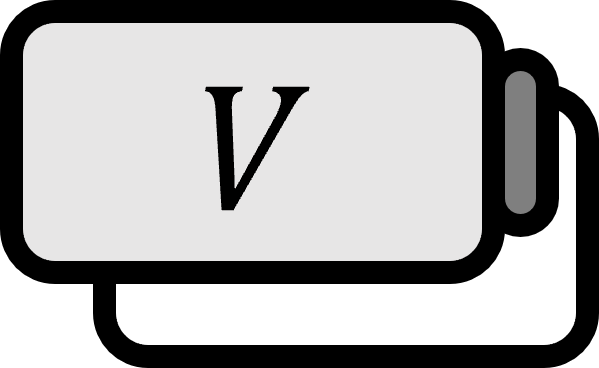
Let’s call $V$ a vector space. A mapping $f$ from $V$ to $\mathbb{C}$ (or $\mathbb{R}$) is called a functional.
$$ f : V \to \mathbb{C} $$
If $f$ is linear, it is called a linear functional.
More Detailed Definitions2
Let’s call $V$ a vector space over the field $F$. Here, the field $F$ itself becomes a $1$-dimensional vector space over $F$. A linear transformation $f : V \to F$ is called a linear functional.
In other words, a linear functional is a linear transformation between a vector space and its field.
Explanation
The first definition given is the most common. Usually, it is not defined as abstractly as the second.
When translating functional into Korean, it becomes ‘범함수’ without much nuance, but it is important to note in English that functional is not an adjective but a noun. Also, the translation of functional as 범함수 (汎函數) is influenced by generalized function.
The distinction from linear operators is only that the codomain is defined as $\mathbb{R}$ or $\mathbb{C}$, but this very difference makes it worthwhile to consider spaces such as dual spaces. Norm $\| \cdot \| = \| \cdot \|_{V}$ already becomes a functional in itself, and considering its usefulness in connection with measure theory is inevitable.
Examples
Trace
Let’s assume $V = M_{n\times n}(\mathbb{R})$. Define the function $f$ as follows.
$$ f : M_{n\times n}(\mathbb{R}) \to \mathbb{R} \quad \text{ by } \quad f(A) = \tr(A) $$
Then $\tr$ is the trace of a matrix. Thus, $f$ is a linear functional.
Fourier Coefficients
Let’s assume $V$ is a vector space of continuous functions that satisfy $f : [0, 2\pi] \to \mathbb{R}$. For a fixed $g \in V$, define $h : V \to \mathbb{R}$ as follows.
$$ h(f) = \dfrac{1}{2\pi} \int_{0}^{2\pi} f(x)g(x)dx $$
Then $h$ is a linear functional. When $g$ is either $\cos nx$ or $\sin nx$, $h(f)$ becomes the Fourier coefficient of $f$.
Coordinate Function
Let’s consider $V$ as a finite-dimensional vector space. Assume $\beta = \left\{ \mathbf{v}_{1}, \dots, \mathbf{v}_{n} \right\}$ is the ordered basis of $V$. Let the coordinate vector of $\mathbf{x} \in V$ be as follows.
$$ [\mathbf{x}]_{\beta} = \begin{bmatrix} a_{1} \\ a_{2} \\ \vdots \\ a_{n} \end{bmatrix} $$
Now, consider the following function for $1 \le i \le n$.
$$ f_{i}(\mathbf{x}) = a_{i} $$
Then $f_{i}$ is a linear functional defined on $V$, called the $i$th coordinate function. Then, $f_{i}(\mathbf{v}_{i}) = \delta_{ij}$ holds true. $\delta_{ij}$ is the Kronecker delta. Coordinate functions play an important role in discussing dual spaces.