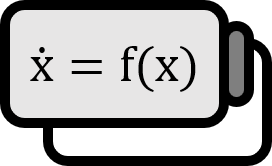Dynamical Model Simulation
Description

The gif above visualizes the Malthusian growth model through agent-based simulation.
Simulation refers to the practice of experimentally implementing a model that explains a phenomenon in a virtual setting. In the context of dynamical models, simulation typically involves methods such as:
- Agent-based Model: An agent-based model is an approach that seeks to emulate the macro world through the micro-actions of each actor (agent). Agents act according to their programming, and can be created in large numbers in some space to represent crowd movements or physical contacts through random walks, or implement selfish transactions in the stock market without spatial characteristics.
- Lattice Model: The lattice model is a method mainly used for visualizing phenomena on a plane, especially in terms of space, by implementing actions on a space divided into grids. Its greatest advantage is that the construction of the model and the handling of the plane make visualization and its explanation simple, naturally reflecting the concept of distance in space. Each cell is often made to interact with adjacent cells, and in that sense, can be seen as a model based on $4$-regular network (up, down, left, right) or $8$-regular network (including diagonals).
- Network-based Model: A network-based model is an approach that seeks to emulate phenomena through the relationships between subjects of the simulation, represented as a network. Networks are usually given as networks obtained from actual data, or random networks that well emulate those.